AML Benchmarking: A Catalyst for Operational Excellence
October 28th, 2024

In the competitive landscape of modern business, achieving operational excellence is a crucial differentiator for any organization striving to stay competitive in an ever-changing environment. One powerful tool that organizations can leverage to achieve this goal is benchmarking. By comparing the organization’s performance metrics to industry metrics, organizations can identify areas for improvement and drive significant enhancements in efficiency and effectiveness.
Understanding Benchmarking
Benchmarking is the process of measuring an organization’s internal processes and performance data against its peers in the same industry. This involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost, efficiency, quality, and speed, and measuring them against those of leading companies or industry averages. This comparison helps identify best practices, set performance standards, and uncover areas where improvements are needed. It provides valuable insights into areas of strength, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. By understanding how an organization stacks up against peers, it can identify gaps, prioritize initiatives, and allocate resources effectively. By continuously benchmarking, organizations can stay competitive, innovate, and enhance their operational effectiveness.
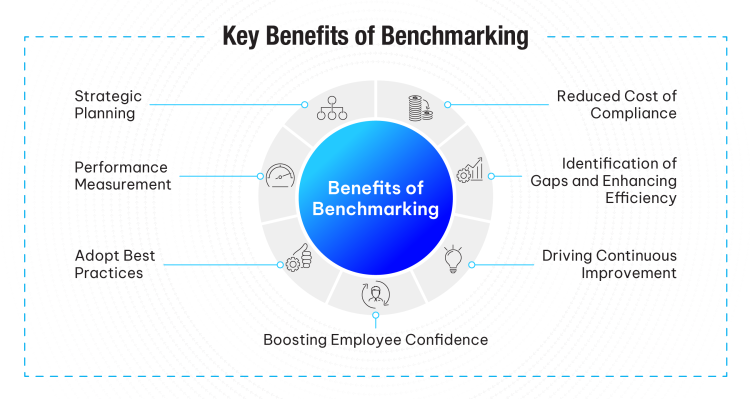
Key Benefits of Benchmarking
- Reduced Cost of Compliance:
Benchmarking plays a crucial role in reducing the overall cost of compliance. By identifying areas for improvement and learning from best practices, organizations can achieve significant gains in efficiency, competitiveness, and overall performance, thereby reducing their overall cost of compliance. This not only reduces the direct costs of compliance but also creates a more efficient and sustainable organization.
- Identification of Gaps and Enhancing Efficiency:
Benchmarking can assist organization in pinpointing inefficiencies and bottlenecks in processes, thereby helping organizations streamline their operations with evidence to support the gaps identified. This leads to improved average handling times, reduction in repetitive tasks, identification of manual process, and improved resource utilization.
- Strategic Planning:
Benchmarking provides data-driven insights that inform strategic decisions, ensuring they are based on industry KPI’s. It also helps in setting a long-term vision by understanding where the organization stands in comparison to industry leaders and what steps are needed to reach the top.
- Performance Measurement:
Benchmarking provides a clear picture of where an organization stands in comparison to its peers. This objective assessment helps in setting realistic performance targets and tracking progress over time.
- Adopt Best Practices:
Benchmarking allows organizations to discover and adopt best practices from industry leaders. By understanding what top-performing companies are doing differently, businesses can implement similar strategies to enhance their own operations.
- Driving Continuous Improvement:
Benchmarking fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By regularly comparing performance metrics and processes, organizations can identify new opportunities for enhancement and stay ahead of the competition.
- Boosting Employee Confidence:
When employees see their organization maintains a culture of continuous improvement and striving for excellence, it can boost the morale and employee engagement for the organization as a whole. Benchmarking, in turn, can lead to improved productivity and better overall performance positively impacting the overall health of the organization.
Key Metrics for AML Benchmarking
- Alert handling time refers to the time taken from when an alert is triggered by the AML system to when it is investigated and resolved. A timely response is essential to prevent financial crimes and maintain regulatory compliance. By effectively benchmarking alert handling time, financial institutions can optimize their AML programs, enhance compliance, and mitigate risks associated with money laundering.
- False Positive Rate is an important metric in evaluating the performance of AML alert systems. It represents the percentage of alerts that were incorrectly triggered, meaning the systems are generating alerts which should not have been generated. A high false positive rate can overwhelm compliance teams and lead to inefficiencies. By benchmarking this metric, organizations can assess the cost-benefit of their AML program and make informed decisions.
- Alert Escalation Rate is a key metric that measures the efficiency of an organization’s alert investigation process. It represents the number of alerts that are escalated to cases for further investigation compared to the total number of alerts generated. Through benchmarking the alert to case ratio, financial institutions can optimize their resource allocation, prioritize high risk alerts, and mitigate the risk of failure to report suspicious activity.
- Alert Volume refer to the total number of alerts generated by a financial institution’s transaction monitoring systems over a specific period. High alert volumes can indicate a robust detection system, but they can also lead to resource strain if not managed properly. Conversely, low alert volumes might suggest that the system is not sensitive enough to detect potential threats. Benchmarking helps in finding the right balance to ensure effective compliance.
- Case to SAR Ratio measures the efficiency of an organization’s investigation and reporting process. It represents the number of suspicious activity reports (SARs) filed compared to the number of cases investigated. By benchmarking case to SAR ratio, organizations can understand the level of risk they pose from different customers groups and ensure compliance with regulatory reporting.
- QA Rate measures the quality and accuracy of AML investigations. A high QA rate indicates that investigations are thorough, accurate, and compliant. Benchmarking the QA rate helps financial institutions ensure that their AML processes are effective, compliant, and continuously improving.
- Assignment Efficiency in AML investigations refers to how effectively alerts and cases are assigned to investigators and how quickly they are resolved. Efficient assignment processes ensure that high-risk cases are prioritized and that investigators are not overwhelmed with an unmanageable workload. Benchmarking assignment efficiency helps financial institutions optimize their processes, ensuring that resources are used effectively and that potential threats are promptly investigated.
How Benchmarking Drives AML Operational Excellence
Benchmarking is a powerful tool that can significantly contribute to operational excellence. By comparing an organization’s performance against industry leaders or best practices, it provides valuable insights for identifying areas of improvement and driving continuous enhancement. Benchmarking acts as a cornerstone of operational excellence through:
- Identifying Performance Gaps:
Comparison: Benchmarking is a strategic tool that enables organizations to compare their performance metrics (e.g., efficiency, quality, cost) against peers, industry leaders or best-in-class practices. This comparison helps identify areas where an organization may be falling short, providing valuable insights for improvement.
Gap Analysis: This comparison helps organizations gain a deeper understanding of their performance, identify areas for improvement, and develop targeted strategies to achieve their goals.
- Setting Realistic Goals:
Aspirational Targets: When organizations benchmark themselves against industry leaders or best-in-class companies, they gain a clear picture of what is possible within their specific field. This knowledge allows them to set goals that are aspirational but attainable, avoiding the pitfalls of setting overly ambitious targets that may lead to frustration and demotivation.
Motivation: Benchmarking can serve as a powerful motivator, inspiring teams to strive for excellence and compete at the highest level. By comparing an organization’s performance against industry leaders or best-in-class practices, benchmarking provides a clear understanding of where the organization stands and where it can aspire to be.
- Prioritizing Improvement Efforts:
Data-Driven Decisions: Benchmarking provides data-driven insights that can help organizations prioritize improvement efforts based on the most significant performance gaps.
Focused Action: By providing data-driven insights, benchmarking helps organizations prioritize improvement efforts effectively, allocate resources wisely, and measure progress toward their goals.
- Measuring Progress:
Tracking Performance: Benchmarking can be used to track progress over time, allowing organizations to assess the effectiveness of their improvement efforts.
Continuous Improvement: By monitoring performance and identifying areas for further improvement, organizations can foster a culture of continuous learning and growth.
Conclusion
Benchmarking is an invaluable strategy that can significantly enhance operational excellence by offering deep insights into industry best practices and performance benchmarks. By meticulously comparing their processes and outcomes with those of leading organizations, companies can pinpoint specific areas that require improvement. This systematic approach not only helps in boosting efficiency but also cultivates a culture of continuous improvement. Ultimately, benchmarking serves as a catalyst for organizations to achieve higher standards of performance, ensuring they remain competitive and innovative.
How NICE Actimize can Help
Let us help you harness the power of benchmarking to drive operational excellence and achieve sustainable success.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn how our expert team can assist you in:
- Identifying areas for improvement
- Setting realistic goals
- Learning from best practices
- Enhancing competitiveness
- Driving continuous improvement